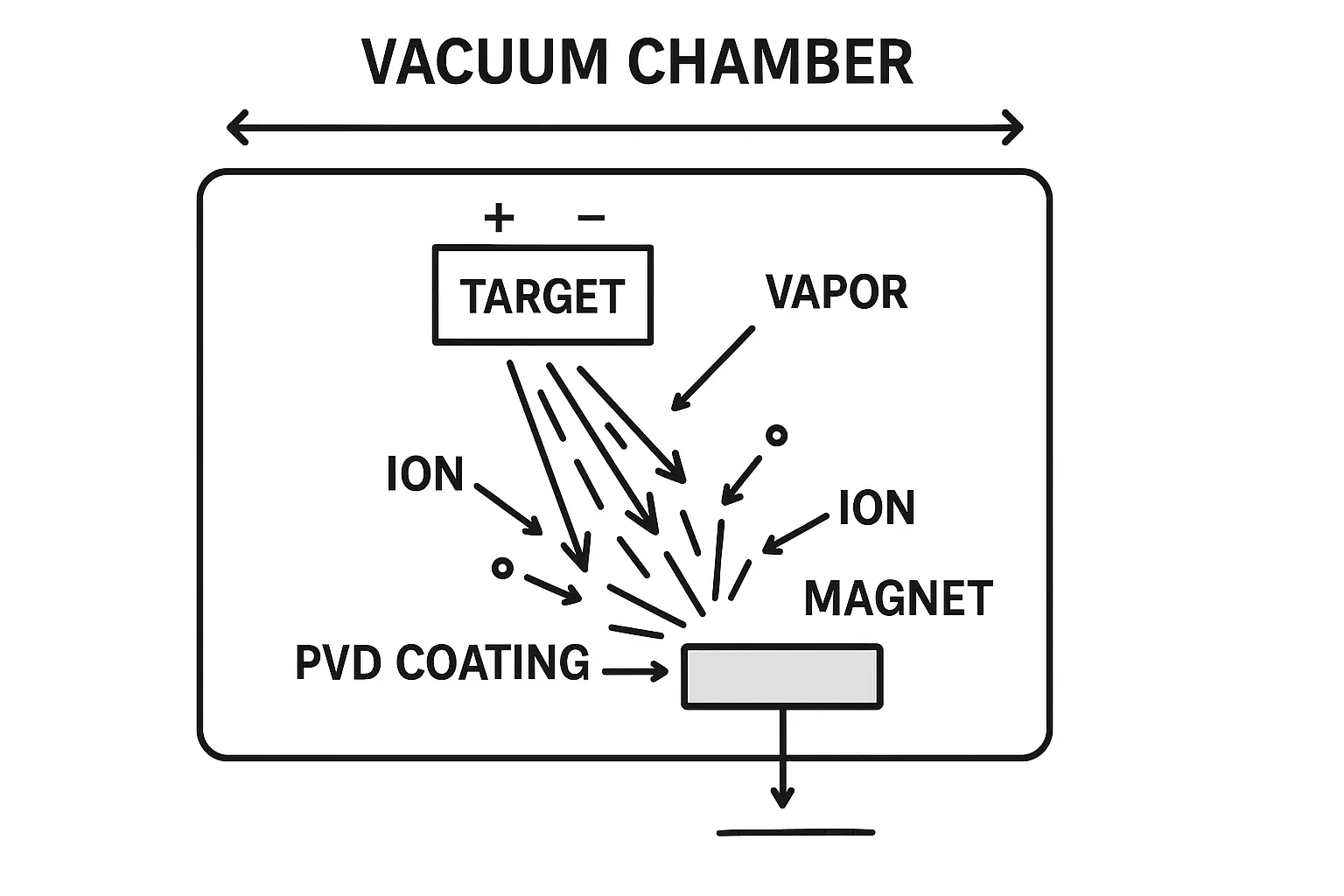
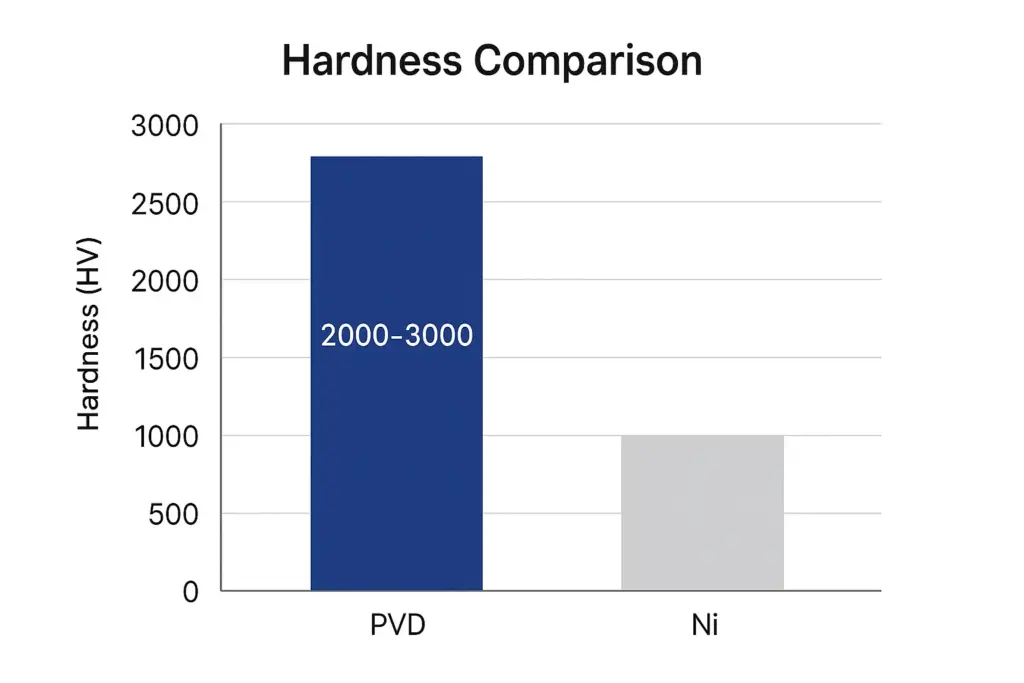
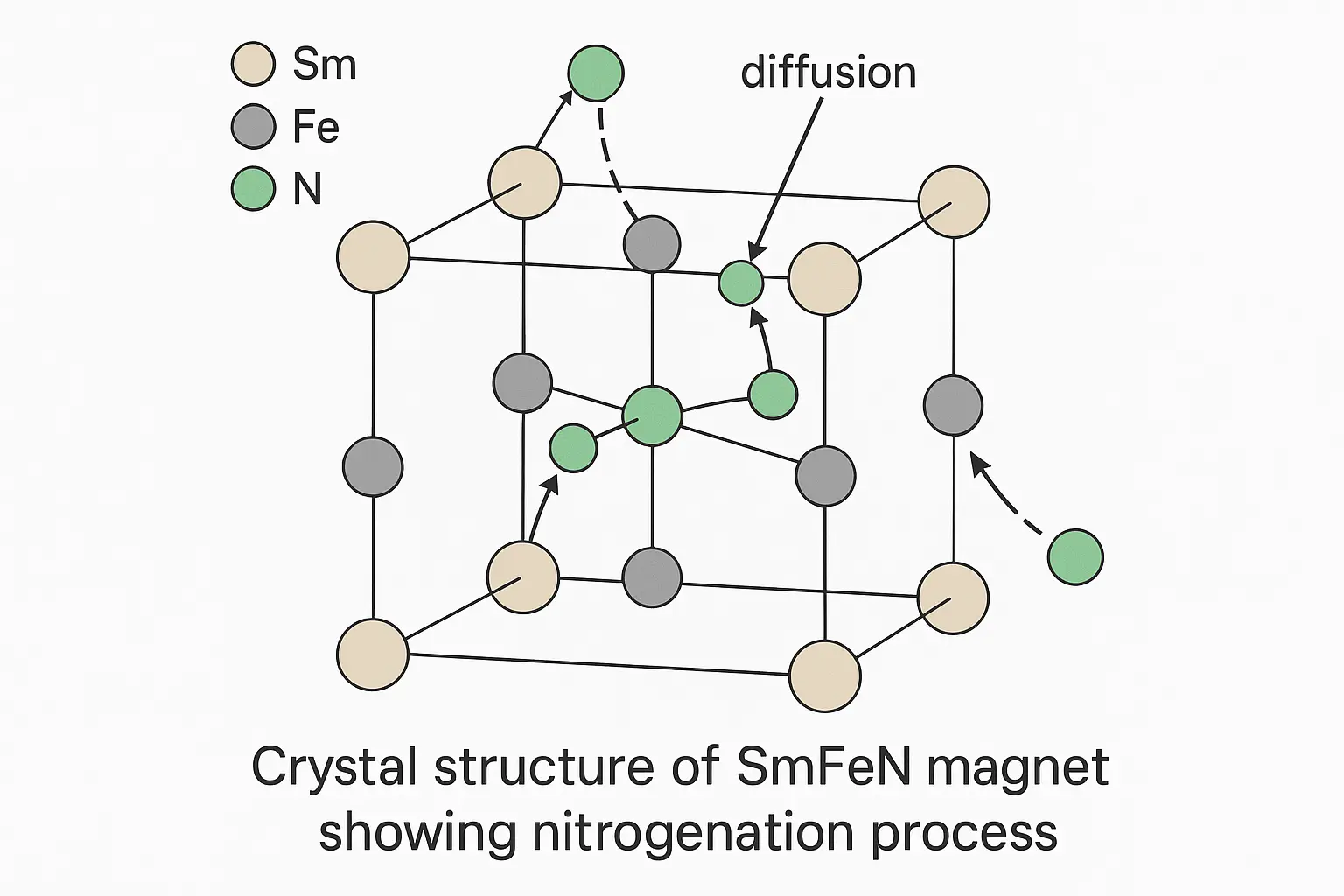
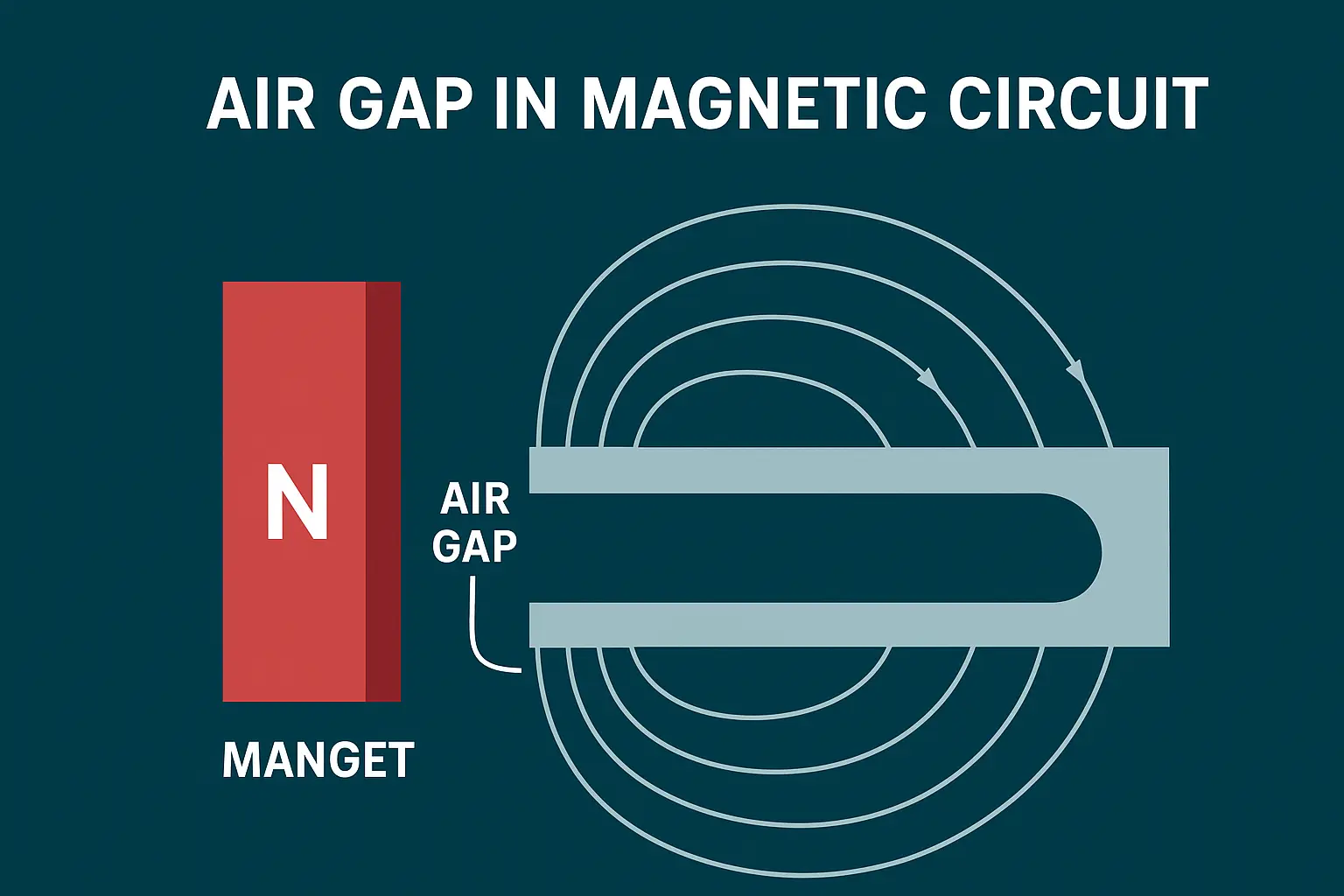
Permanent magnets are essential in countless applications — from motors, loudspeakers, and MRI machines to fridge magnets and magnetic tools. What makes them remarkable is their ability to retain magnetism for decades or even centuries. But why can they “remember” their magnetism so well, while other metals lose it instantly?
To understand this, we first need to explore the different types of magnetic materials, how they are classified, and the physical principles that allow permanent magnets to resist demagnetization.
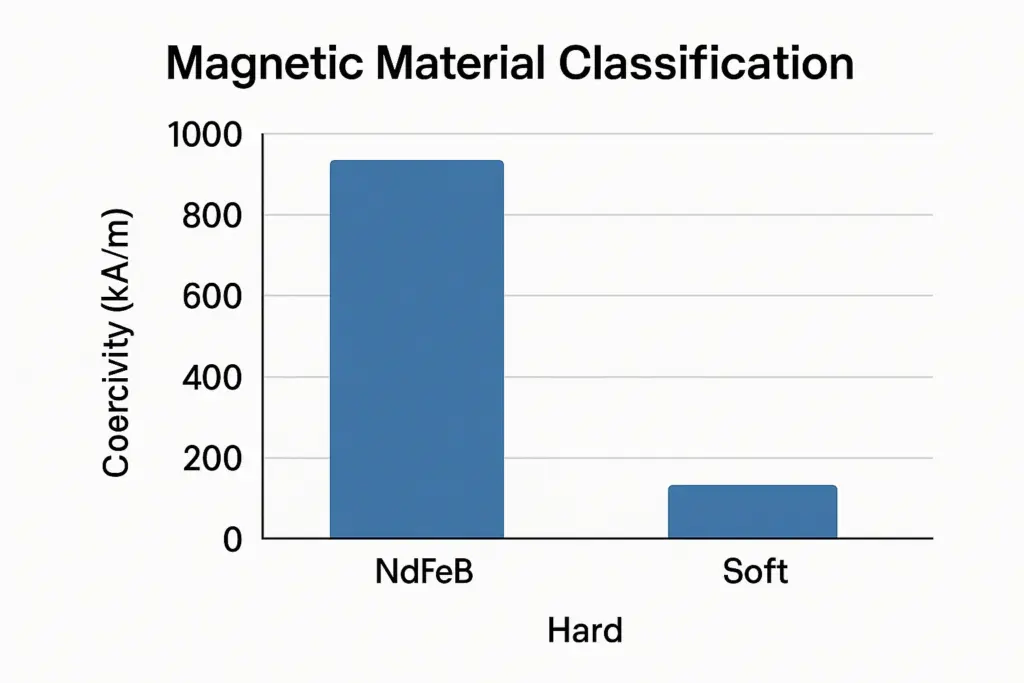
1. Magnetic Material Classification: Hard vs. Soft Magnetic Materials
Magnetic materials can be broadly divided into permanent (hard) and soft magnetic materials based on their ability to retain magnetism.
| Type | Coercivity | Key Feature | Example Materials | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent (Hard) Magnetic Materials | High (hundreds to thousands of kA/m) | Retain magnetism for long periods | Neodymium (NdFeB), Samarium Cobalt (SmCo), Ferrite, Alnico | Motors, generators, sensors, magnetic locks |
| Soft Magnetic Materials | Low (few A/m to tens of A/m) | Easily magnetized and demagnetized | Pure iron, silicon steel, permalloy | Transformers, inductors, electromagnets |
Key Difference: Coercivity
- Coercivity is the measure of a material’s resistance to losing its magnetism when an opposing magnetic field is applied.
- Permanent magnets have high coercivity, meaning it takes a very strong reverse field to demagnetize them.
- Soft magnets have low coercivity, which makes them ideal for applications requiring rapid magnetization and demagnetization cycles.
2. Why Permanent Magnets Stay Magnetic
(1) High Coercivity – Resistance to Reverse Fields
Permanent magnets are made from materials whose atomic structure and chemical composition give them very high coercivity.
Example:
- Neodymium magnets can have coercivity values exceeding 1000 kA/m.
- In everyday life, typical stray magnetic fields are far too weak to affect them.
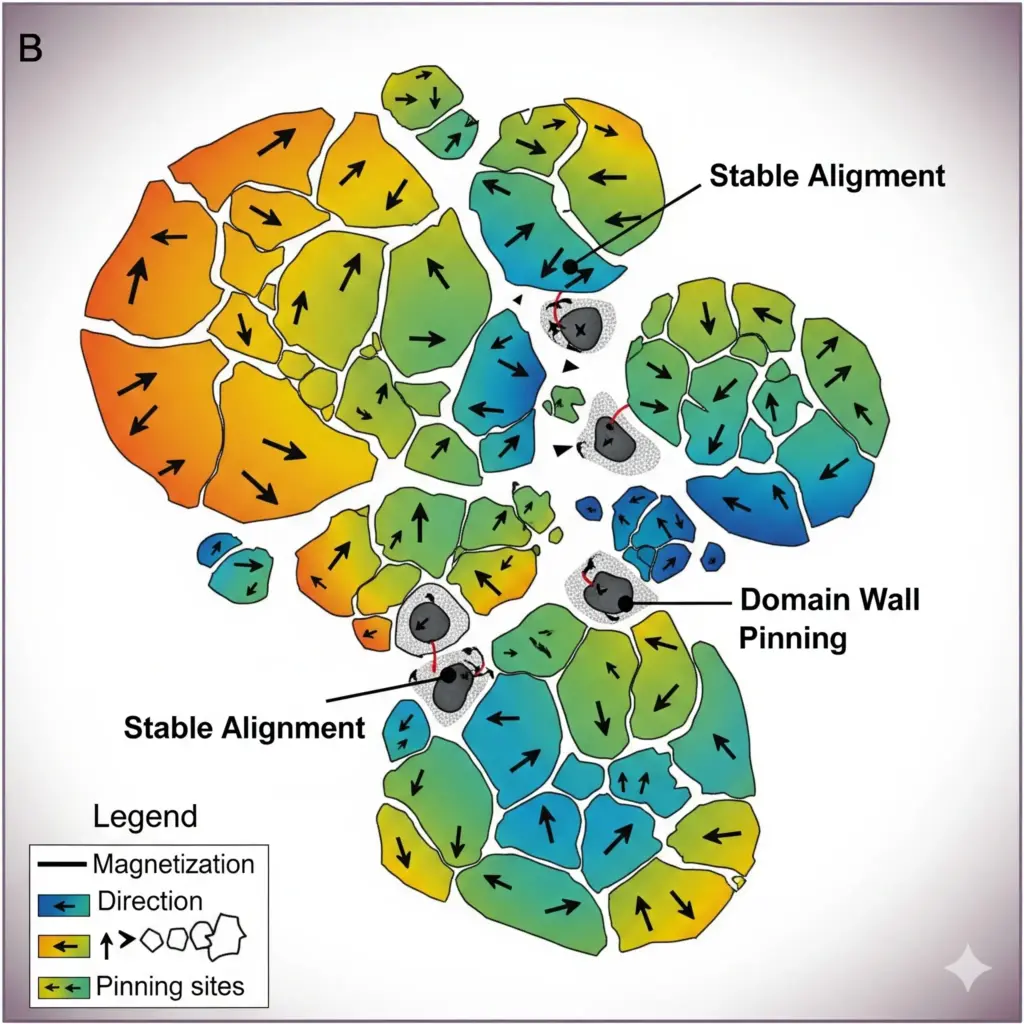
(2) Stable Magnetic Domain Alignment
Inside a magnetic material, tiny regions called magnetic domains each act like a small magnet.
- In permanent magnets, these domains are “locked” in one direction during manufacturing.
- This alignment is held in place by magnetic anisotropy — a property that makes certain crystal orientations energetically more favorable.
In contrast, in soft magnets, domains can shift or flip easily under even weak opposing fields.
(3) High Curie Temperature – Thermal Stability
The Curie temperature is the point at which a magnet loses its magnetic order due to heat.
- Alnico: 750–860 °C (1382–1580 °F)
- Ferrite: ~450 °C (842 °F)
- NdFeB: ~310 °C (590 °F)
Below this temperature, the atomic magnetic moments remain aligned. The higher the Curie temperature, the better the magnet resists thermal demagnetization.
(4) Optimized Microstructure
Modern permanent magnets are engineered to trap magnetic domains in place:
- Fine-grained crystals reduce the movement of domain walls.
- Grain boundary phases act as barriers against demagnetization.
- Example: Nd₂Fe₁₄B crystals in neodymium magnets are surrounded by Nd-rich grain boundaries that block reversal of domain alignment.
(5) Resistance to Environmental Factors
While permanent magnets are stable, they can lose magnetism due to:
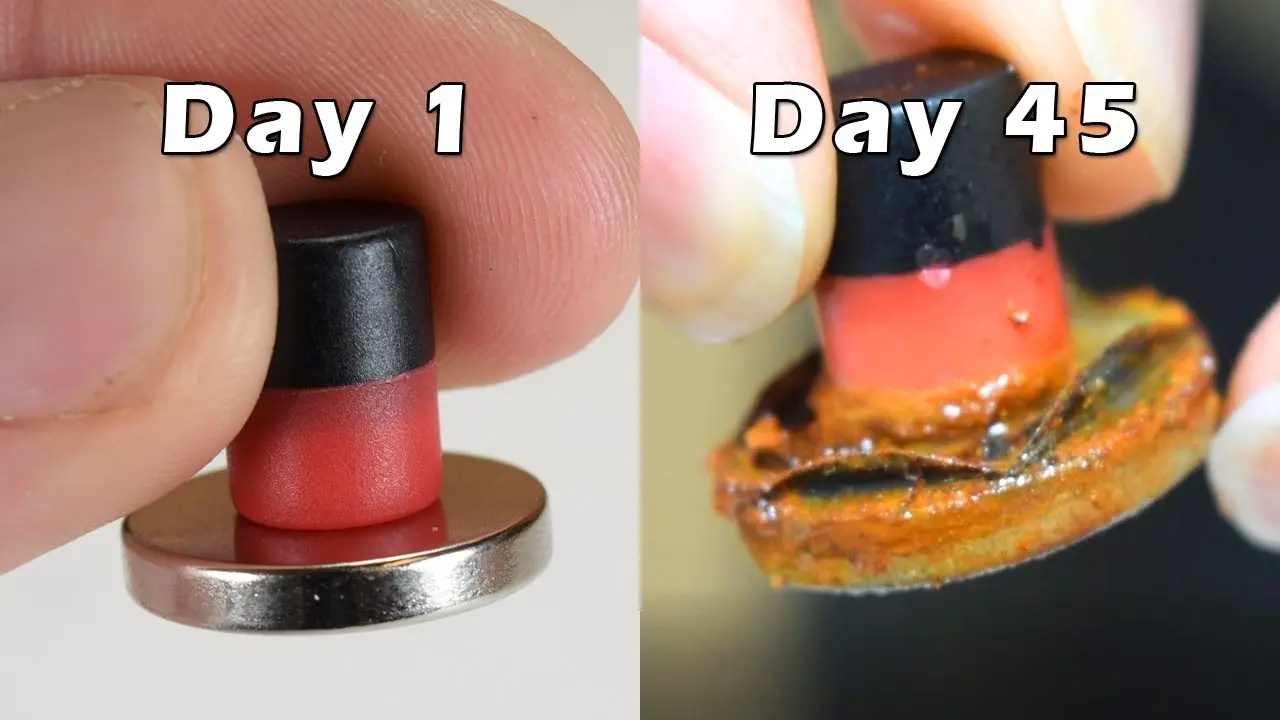
- Corrosion (especially NdFeB, which requires nickel or epoxy coating)
- Severe mechanical shock
- Exposure to very strong reverse magnetic fields
With proper coating, handling, and storage, high-quality permanent magnets can maintain over 95% of their original magnetism even after decades.
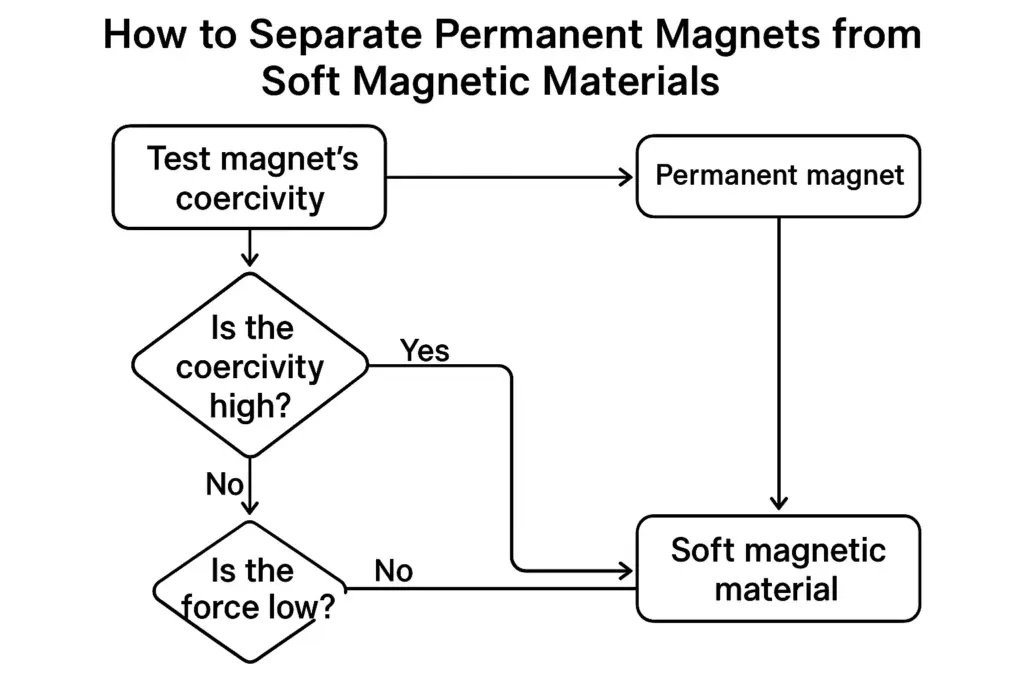
3. How to Separate Permanent Magnets from Soft Magnetic Materials
In industrial and laboratory settings, distinguishing between permanent magnets and soft magnetic materials is important:
| Method | Observation |
|---|---|
| Check Retentivity | After removing from a magnetizing field, a permanent magnet keeps strong magnetism; soft magnet loses it quickly. |
| Coercivity Testing | Apply a reverse field and measure the demagnetizing force needed. |
| Magnet Pull Test | Compare the holding force before and after exposure to opposing fields. |
| Material Identification | Use chemical composition analysis (NdFeB, SmCo, Alnico = hard; pure Fe, permalloy = soft). |
4. The Science Behind Coercivity
Coercivity depends on:
- Magnetocrystalline anisotropy – Atomic lattice prefers specific spin directions.
- Microstructural defects – Can either pin domain walls (in hard magnets) or allow free movement (in soft magnets).
- Chemical composition – Elements like cobalt, rare earths, and aluminum increase coercivity.
High coercivity means a magnet “remembers” its original magnetization, making it resistant to accidental demagnetization from environmental fields or minor shocks.
5. Summary
Permanent magnets remain magnetic because:
- They have high coercivity, resisting reverse fields.
- Their magnetic domains are strongly locked in place.
- They have a high Curie temperature, resisting thermal effects.
- Their microstructure is optimized for stability.
- They are protected from corrosion and mechanical damage.
By contrast, soft magnetic materials are designed to switch magnetism on and off easily, making them ideal for electromagnets and transformer cores — but not for long-term magnetic retention.
If you need expert advice on choosing the right magnet — whether high-coercivity permanent magnets for motors, or soft magnetic cores for transformers — feel free to contact us. Our engineering team can provide both technical guidance and customized magnet solutions.